Ask the Admins: What is Activation Lock?
What is Activation Lock and how does it work? Consider this: a field marketer misplaces a company MacBook at a conference. Before IT can respond, someone powers it on and attempts to reset it for resale. This is more than a lost device—it’s an immediate operational and security risk. A single Mac may contain project files, proprietary creative assets, or authenticated access to systems like Salesforce or HubSpot, exposing sensitive data and creating compliance gaps the moment it leaves your control.
Activation Lock—Apple’s built-in security control—is designed to prevent exactly this. As the second line of defense behind passcodes and screen locks, Activation Lock ensures a device cannot be reactivated or repurposed without the proper credentials or, in managed environments, a valid MDM-issued bypass code.
In this guide, we’ll break down what Activation Lock is, how it works, the differences between user-driven and MDM-managed implementations, and what IT teams need to know to manage it effectively across their fleet.
What is Activation Lock?
Activation Lock is an Apple security feature designed to prevent unauthorized use of a device after it’s lost, stolen, or erased. Its core purpose is simple: a device cannot be reactivated unless the correct Apple ID credentials—or, in a managed environment, an MDM-issued bypass code—are provided.
Even if someone wipes the device or puts it into recovery mode, Activation Lock blocks setup and reactivation, preventing bad actors from repurposing, reselling, or activating the device for their own use.
User-enabled vs MDM-managed Activation Lock
There are two versions of Activation Lock, and the behavior differs depending on ownership and management:
- User-enabled Activation Lock: Triggered when a user signs into iCloud and enables Find My on the device. This is common on personally owned or lightly managed devices.
- MDM-managed Activation Lock: Automatically enabled through an MDM platform—such as Addigy—during Automated Device Enrollment (ADE). This allows IT to enforce lock settings, retrieve or clear bypass codes, and ensure devices remain recoverable at scale.
With Addigy MDM and ABM, Activation Lock is tied to the organization, not the individual, so IT can always recover, repurpose, or decommission a device without user participation.
Supported Devices
Apple Activation Lock is available on:
- iOS 7.1+
- iPadOS 13+
- macOS 10.15+ devices with a T2 Security Chip or Apple Silicon
Understanding these distinctions of where Activation Lock is supported is essential for any organization looking to secure its Apple fleet and maintain control of devices throughout their lifecycle.
Note: Addigy’s MDM supports Activation Lock management for all current Apple devices, including those running iOS 7.1+, iPadOS 13+, and macOS 10.15+ with T2 or Apple Silicon chips.
How Activation Lock Works
Activation Lock leverages Apple’s Find My infrastructure, which ties a device’s hardware identifier to an Apple ID or an MDM-managed Activation Lock configuration. Once Find My is enabled—either manually or automatically through ADE—the device is linked to an activation record stored on Apple’s activation servers.
What Happens When a Device Is Locked?
When Activation Lock is active:
- The device stores cryptographic activation data that links the hardware to an Apple ID (user-enabled) or an MDM-managed Activation Lock token (enterprise-managed).
- If the device is erased, whether through Settings, macOS Recovery, or DFU mode, the device must contact Apple’s activation servers when attempting to boot into Setup Assistant.
- Apple’s activation server checks the activation record. If the device is marked as locked, setup is halted until the correct Apple ID credentials—or an MDM-issued bypass code—are entered.
- The device remains unusable and displays a message indicating it is Activation Locked and requires authentication to continue.
This mechanism ensures the device cannot be reactivated or repurposed without explicit authorization, even after a complete wipe.
Activation Lock Experience As The Device Owner
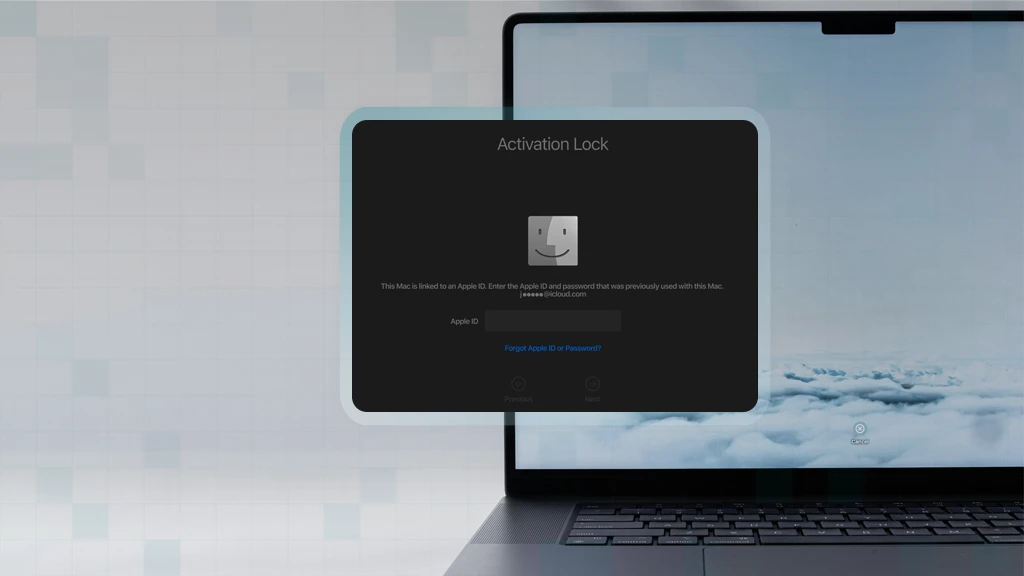
- For end users: A locked device boots to an Activation Lock screen, prompting for the Apple ID and password previously associated with the device.
- For IT administrators: In environments using MDM-managed Activation Lock, admins can view or generate a bypass code directly from their MDM platform. This allows IT to unlock, recover, or repurpose devices—even if an employee is unavailable or no longer with the organization. See how it works in Addigy.
Types of Activation Lock
Activation Lock can operate in two distinct modes depending on how a device is owned and enrolled. Understanding the differences is essential for preventing unexpected lockouts and ensuring IT maintains control over corporate hardware.
User-Based Activation Lock
User-based Activation Lock is enabled when an individual signs into iCloud and turns on Find My. This behavior is common on personally owned devices or corporate devices that allow users to sign in with personal Apple IDs.
Key characteristics:
- The device becomes tied to the user’s Apple ID, not the organization.
- If the user leaves the company or forgets their Apple ID password, the device may become locked and unrecoverable without their credentials.
- MDM may be able to retrieve a Device Activation Lock Bypass Code, but only if Find My was enabled after enrollment and supervision conditions were met—so availability is not guaranteed.
When it occurs: Often on BYOD or improperly supervised corporate devices where users are allowed to sign into personal iCloud accounts.
MDM Activation Lock
MDM Activation Lock is the recommended model for corporate fleets. It is enforced through an MDM solution via Automated Device Enrollment (ADE) in Apple Business Manager.
Key characteristics:
- The device is supervised and managed by the organization from first boot.
- Activation Lock is enabled by the MDM server, not the end user.
- A Server Activation Lock Bypass Code is always available, ensuring IT can unlock or repurpose a wiped device.
- No Apple ID is required to protect or recover the device.
When it applies: Corporate-owned devices enrolled through Automated Device Enrollment (ADE).
Key Differences Between User-Based and MDM Activation Lock
| Feature | User-Based | MDM | Addigy MDM Advantage |
| Linked to Apple ID | Yes: tied to the user’s iCloud account | No: tied to MDM/Server record | No: central management |
| Bypass Code Availability | Not always guaranteed | Always available to IT | Automated storage and retrieval |
| Best For | BYOD / Personalized devices | Corporate fleets | MSPs, mid-size, enterprise fleets |
| Risk of Lockout | High if user leaves or forgets credentials | Low: IT retains full recovery control | Low: IT retains full recovery control |
| IT Control | Limited | Full administrative control | Full administrative control + delegated access; Single-pane dashboard for all devices |
Managing Activation Lock with MDM
MDM Activation Lock—also known as organization-linked Activation Lock—gives IT full control over Activation Lock enforcement and recovery. To support this model, devices must meet specific supervision and enrollment requirements.
Requirements for MDM Activation Lock
To enable Activation Lock through MDM, the device must:
- Be supervised
- Be assigned in Apple Business Manager (ABM) or Apple School Manager (ASM)
Be enrolled using Automated Device Enrollment (ADE) - Use macOS 10.15+ (with T2/Apple Silicon) or iOS/iPadOS 13
Enabling Activation Lock in Automated Device Enrollment
During ADE configuration, administrators choose whether supervised devices allow MDM-managed Activation Lock. Because Activation Lock is disabled by default on supervised devices, the MDM must explicitly enable it.
When Activation Lock is enabled:
- The MDM escrows a Server Activation Lock Bypass Code, which Apple confirms allows activation “without the Apple ID and password.”
- Apple stores an organization-linked Activation Lock record that persists even if no user signs into iCloud.
- Activation Lock behavior becomes consistent and centrally controlled across the fleet.
This ensures predictable protection regardless of user behavior.
Viewing & Managing Bypass Codes
In Addigy and other enterprise MDMs:
- Each supervised device generates a unique bypass code.
- Codes can be viewed in the device record.
- IT can export or store them in a secure vault for redundancy.
Bypass codes give IT the ability to unlock, recover, or repurpose a device without relying on end-user credentials. Addigy’s platform ensures every supervised device’s bypass code is available for immediate export, vaulting, or use – removing guesswork from Incident response
Disabling Activation Lock via ABM/ASM
When a device needs to be repurposed, transferred, or decommissioned, IT can clear Activation Lock server-side:
- Sign in to Apple Business Manager
- Locate the device
- Select Clear Activation Lock
This ensures the device remains recoverable—even if it was wiped before IT intervened.
Best Practices for Bypass Code Storage
- Store bypass codes in an encrypted IT vault or secure MDM notes.
- Automate code retrieval during enrollment.
- Audit bypass code availability during device lifecycle events.
- Avoid user-based Activation Lock on corporate devices.
For organizations managing dozens or thousands of Macs and iOS devices, using the MDM Activation Lock is essential to maintaining control and preventing device loss from turning into operational or security risk. With tools like Addigy MDM, IT can instantly check device status, retrieve bypass codes, and secure lost hardware before data exposure becomes a crisis.
Common Activation Lock Challenges and Solutions
Activation Lock is effective, but misconfigurations or user behavior can still create challenges for IT teams. Below are the most common issues organizations encounter—and the practical steps to resolve them quickly.
Lost or Missing Bypass Codes
- Problem: An admin fails to export or store the bypass code during enrollment.
- Solution: Retrieve from the MDM if available. If user-enabled, the only recovery option may be Apple ID verification and proof of purchase.
User-Enabled Activation Lock on Corporate Devices
- Problem: Employees sign into personal iCloud accounts and accidentally lock the device.
- Solution: Restrict personal iCloud sign-in on corporate hardware. Re-enroll devices via ABM to restore proper supervision.
How does an IT admin retain device ownership without an MDM? It’s tricky business but see the Reddit thread here.
Device Decommissioning With Activation Lock Enabled
- Problem: An offboarded employee leaves without removing their Apple ID.
- Solution: Use the MDM or ABM to clear Activation Lock before wiping the device. Store bypass codes for all corporate-owned hardware.
Troubleshooting Locked macOS Devices
- Problem: Some T2 and Apple Silicon Macs display different lock screens.
- Solution: Enter the bypass code. If unsuccessful, reattempt after Internet Recovery prompts complete. Confirm the device appears in ABM.
By standardizing bypass code management, restricting personal iCloud use, and enforcing supervised enrollment, IT teams can prevent most Activation Lock issues before they disrupt operations.
The Power of Activation Lock
Activation Lock is a powerful, hardware-level security feature that protects corporate devices from unauthorized use, resale, or post-wipe reactivation. When managed through MDM, it gives IT full lifecycle control—ensuring devices remain recoverable and secure, regardless of user behavior.
Understanding the differences between user-based and device-based Activation Lock, enabling it through Automated Device Enrollment, and maintaining secure bypass code workflows are essential steps for any modern Apple device strategy.
Ready to take control of Activation Lock across your fleet? Start a free trial with Addigy.
For deeper technical guidance, review Addigy support resources: